Researchers from the University of the Philippines (UP) Diliman have made a significant breakthrough in the study of prostate cancer by identifying a key protein that drives the disease towards its most aggressive form, neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC). The protein, known as CYB561, has been found to play a dual role in promoting the growth and survival of treatment-resistant prostate cancer cells.
CYB561: Insights into its Role and Impact
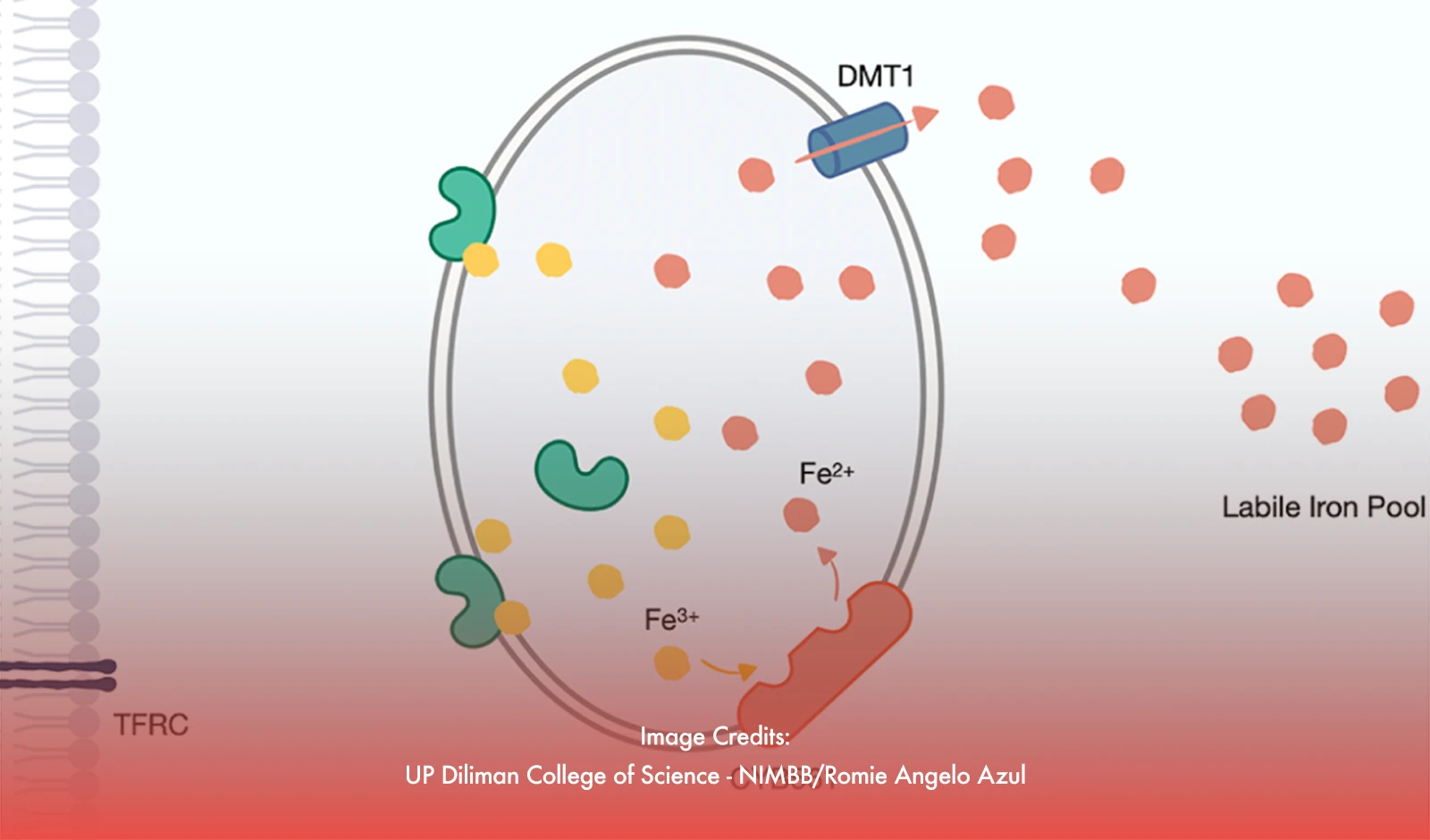
Led by Dr. Pia Bagamasbad and her team at UP Diliman's College of Science National Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, the research highlighted CYB561's critical functions. "CYB561 activates specific growth factors crucial for cancer cell proliferation and manages iron levels necessary for various cellular processes," explained Dr. Bagamasbad. This dual action enables prostate cancer cells to thrive even under conditions where they are deprived of male hormones, which are typically targeted in conventional therapies like androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).
Potential Implications and Future Directions
The discovery that CYB561 also facilitates the conversion of iron into an active form essential for cancer growth suggests its potential as a therapeutic target. In experiments, suppressing CYB561 led to increased sensitivity of cancer cells to ADT and slowed the progression towards NEPC. This finding opens avenues for developing targeted therapies aimed at disrupting CYB561 activity, potentially improving treatment outcomes for patients with aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
Moving forward, the research team plans to validate these findings through animal studies and clinical samples. They also aim to investigate whether populations, such as Filipinos, who may have a higher susceptibility to developing castration-resistant prostate cancer and NEPC, exhibit unique genetic factors that influence CYB561 activity.
This research not only enhances our understanding of prostate cancer biology but also underscores the importance of personalized medicine approaches in oncology. By targeting specific molecular mechanisms like CYB561, researchers hope to advance towards more effective treatments that can ultimately benefit patients worldwide.