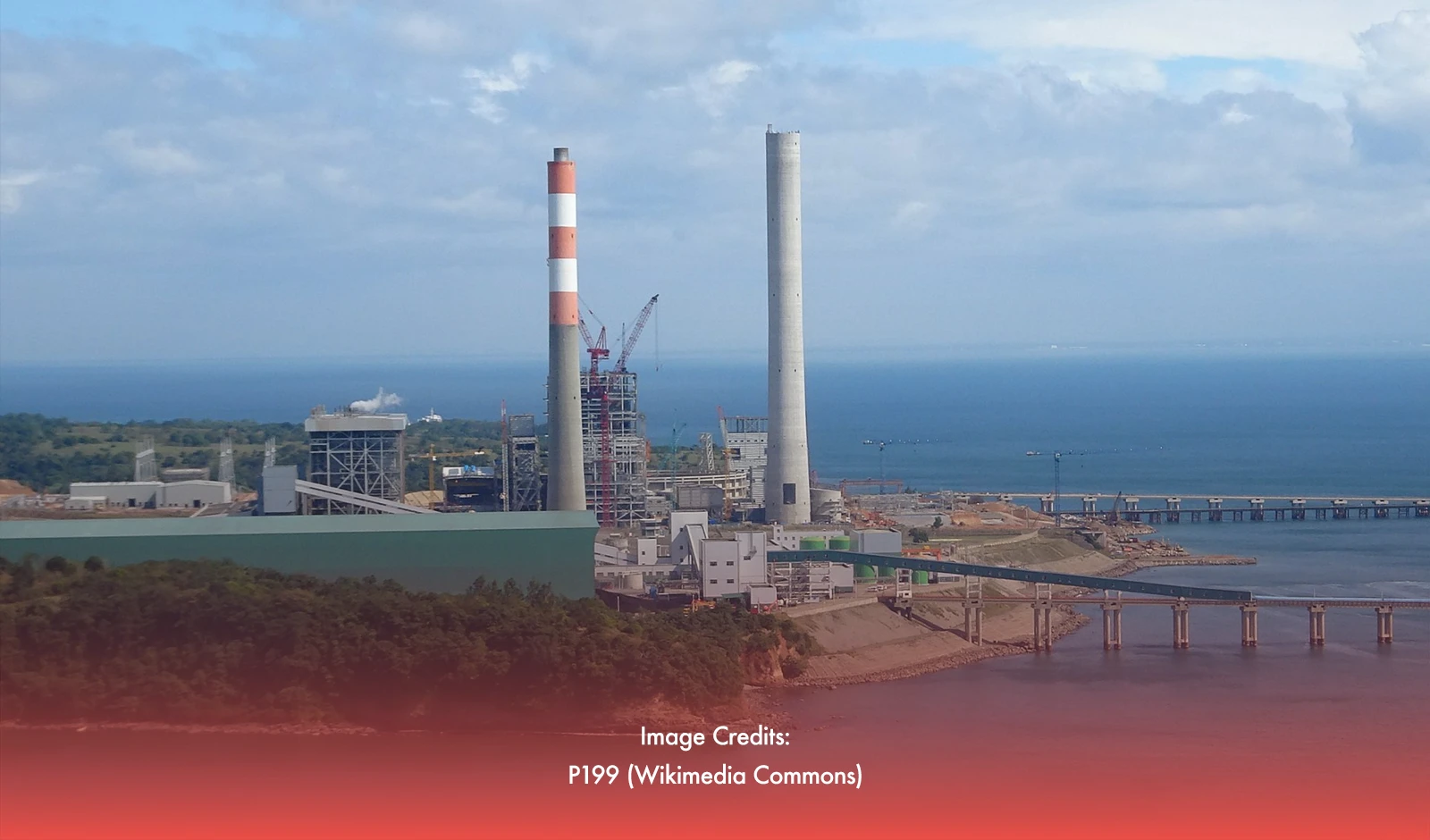
Despite the rise of cleaner energy options, coal-fired power plants continue to dominate the Philippines, serving as the primary source of electricity across the archipelago. According to data from the Department of Energy (DOE), coal maintains its position as the top contributor to the country's power grid, providing a substantial portion of its energy needs.
Coal remains a reliable and cost-effective source of power, ensuring a stable supply of electricity to meet the growing demands of industries, businesses, and households. Its continued prominence underscores its vital role in driving the Philippines' economic development and supporting its infrastructure.
While there is increasing global emphasis on transitioning to renewable energy sources to mitigate climate change and reduce environmental impact, coal's prevalence in the Philippines reflects the complex energy challenges facing the nation. Factors such as the abundance of coal reserves, existing infrastructure, and the need for affordable energy solutions contribute to its enduring significance.
Renewables Catching Up: A Brighter Energy Future
Amidst coal's dominance, renewable energy sources are gradually gaining momentum, signaling a promising shift towards a more sustainable energy future. Solar and hydropower emerge as frontrunners in this transition, with significant increases in their capacity in recent years.
Solar power, in particular, has seen remarkable growth, fueled by technological advancements and favorable government policies promoting renewable energy adoption. The proliferation of solar installations across the country reflects a growing awareness of the benefits of clean energy and a desire to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Hydropower, another renewable energy source, has also expanded its capacity, leveraging the Philippines' abundant water resources to generate electricity. The development of hydropower projects not only contributes to the diversification of the energy mix but also harnesses the natural power of water to generate clean and renewable electricity.
Off-Grid Changes: More Energy Options
In off-grid areas where access to electricity is limited, there is a notable diversification of energy sources, reflecting efforts to improve energy accessibility and reliability. While oil-based power plants traditionally dominated off-grid setups, there is a growing presence of renewable energy solutions, providing communities with alternative and sustainable electricity options.
Despite the challenges posed by geographical isolation and limited infrastructure, off-grid communities are embracing renewable energy technologies such as solar panels and micro-hydro systems. These decentralized energy solutions not only reduce dependence on imported fuels but also empower communities to harness local resources for energy generation, promoting self-sufficiency and resilience.